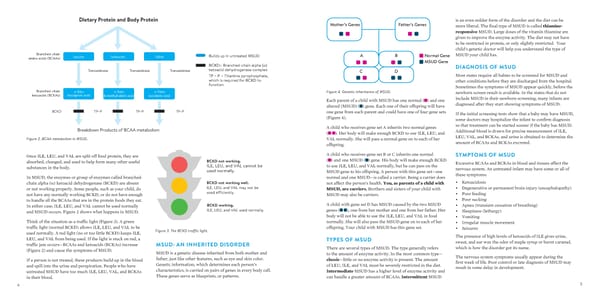
Dietary Protein and Body Protein is an even milder form of the disorder and the diet can be Mother’s Genes Father’s Genes more liberal. The final type of MSUD is called thiamine- responsive MSUD. Large doses of the vitamin thiamine are given to improve the enzyme activity. The diet may not have to be restricted in protein, or only slightly restricted. Your child’s genetic doctor will help you understand the type of Branched-chain Leucine Isoleucine Valine Builds up in untreated MSUD A B Normal Gene MSUD your child has. amino acids (BCAAs) MSUD Gene BCKD= Branched-chain alpha (α) DIAGNOSIS OF MSUD Transaminase Transaminase Transaminase ketoacid dehydrogenase complex C D TP ~ P = Thiamine pyrophosphate, Most states require all babies to be screened for MSUD and which is required for BCKD to other conditions before they are discharged from the hospital. function Sometimes the symptoms of MSUD appear quickly, before the Branched-chain α-Keto- α-Keto- α-Keto- Figure 4. Genetic inheritance of MSUD. newborn screen result is available. In the states that do not ketoacids (BCKAs) isocaproic acid β-methylvaleric acid isovaleric acid include MSUD in their newborn screening, many infants are Each parent of a child with MSUD has one normal ( ) and one diagnosed after they start showing symptoms of MSUD. altered (MSUD) ( ) gene. Each one of their offspring will have BCKD TP~P TP~P TP~P one gene from each parent and could have one of four gene sets If the initial screening tests show that a baby may have MSUD, (Figure 4). some doctors may hospitalize the infant to confirm diagnosis A child who receives gene set A inherits two normal genes so that treatment can be started sooner if the baby has MSUD. Breakdown Products of BCAA metabolism ( ). Her body will make enough BCKD to use ILE, LEU, and Additional blood is drawn for precise measurement of ILE, Figure 2. BCAA metabolism in MSUD. VAL normally. She will pass a normal gene on to each of her LEU, VAL, and BCKAs, and urine is obtained to determine the offspring. amount of BCAAs and BCKAs excreted. Once ILE, LEU, and VAL are split off food protein, they are A child who receives gene set B or C inherits one normal SYMPTOMS OF MSUD absorbed, changed, and used to help form many other useful BCKD not working. ( ) and one MSUD ( ) gene. His body will make enough BCKD Excessive BCAAs and BCKAs in blood and tissues affect the substances in the body. ILE, LEU, and VAL cannot be to use ILE, LEU, and VAL normally, but he can pass on the nervous system. An untreated infant may have some or all of used normally . MSUD gene to his offspring. A person with this gene set—one these symptoms: In MSUD, the enzymes or group of enzymes called branched- normal and one MSUD—is called a carrier. Being a carrier does α) ketoacid dehydrogenase (BCKD) are absent BCKD not working well. • Ketoacidosis chain alpha ( not affect the person’s health. You, as parents of a child with or not working properly. Some people, such as your child, do ILE, LEU, and VAL may not be MSUD, are carriers. Brothers and sisters of your child with • Degenerative or permanent brain injury (encephalopathy) not have any normally working BCKD, or do not have enough used efficiently. MSUD may also be carriers. • Poor feeding to handle all the BCAAs that are in the protein foods they eat. • Poor sucking In either case, ILE, LEU, and VAL cannot be used normally BCKD working. A child with gene set D has MSUD caused by the two MSUD • Apnea (transient cessation of breathing) and MSUD occurs. Figure 2 shows what happens in MSUD. ILE, LEU, and VAL used normally. genes ( ), one from her mother and one from her father. Her • Sleepiness (lethargy) body will not be able to use the ILE, LEU, and VAL in food • Vomiting Think of the situation as a traffic light (Figure 3). A green normally. She will also pass the MSUD gene on to each of her • Irregular muscle movement traffic light (normal BCKD) allows ILE, LEU, and VAL to be Figure 3. The BCKD traffic light. offspring. Your child with MSUD has this gene set. • Seizures used normally. A red light (no or too little BCKD) keeps ILE, The presence of high levels of ketoacids of ILE gives urine, LEU, and VAL from being used. If the light is stuck on red, a TYPES OF MSUD sweat, and ear wax the odor of maple syrup or burnt caramel, traffic jam occurs—BCAAs and ketoacids (BCKAs) increase MSUD: AN INHERITED DISORDER There are several types of MSUD. The type generally refers which is how the disorder got its name. (Figure 2) and cause the symptoms of MSUD. MSUD is a genetic disease inherited from both mother and to the amount of enzyme activity. In the most common type— If a person is not treated, these products build up in the blood father, just like other features, such as eye and skin color. classic—little or no enzyme activity is present. The amount The nervous system symptoms usually appear during the and spill into the urine and perspiration. People who have Genetic information, which determines each person’s of LEU, ILE, and VAL must be severely restricted in the diet. first week of life. Poor control or late diagnosis of MSUD may untreated MSUD have too much ILE, LEU, VAL, and BCKAs characteristics, is carried on pairs of genes in every body cell. Intermediate MSUD has a higher level of enzyme activity and result in some delay in development. in their blood. These genes serve as blueprints, or patterns. can handle a greater amount of BCAAs. Intermittent MSUD 4 5
 A Guide for Understanding Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD) Page 2 Page 4
A Guide for Understanding Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD) Page 2 Page 4