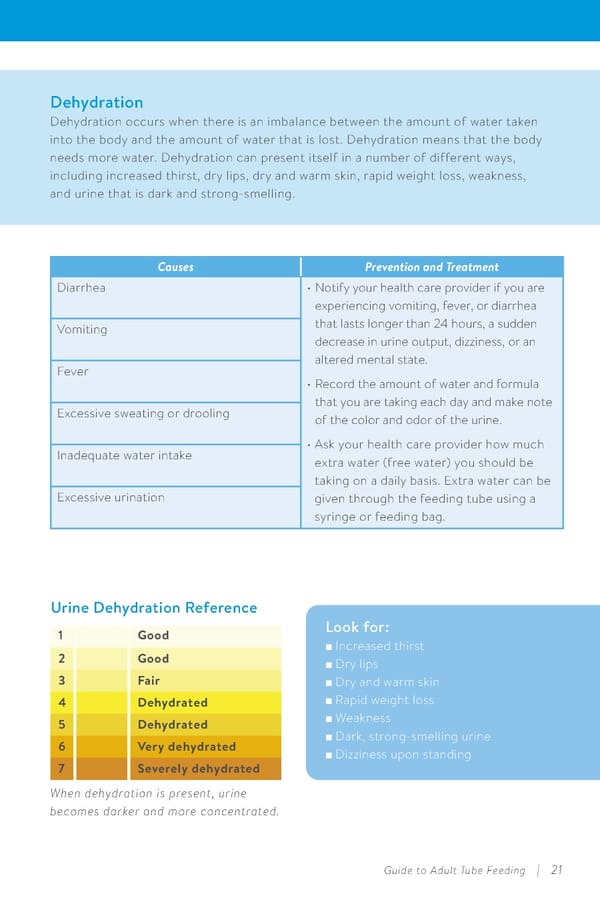
Dehydration Dehydration occurs when there is an imbalance between the amount of water taken into the body and the amount of water that is lost. Dehydration means that the body needs more water. Dehydration can present itself in a number of different ways, including increased thirst, dry lips, dry and warm skin, rapid weight loss, weakness, and urine that is dark and strong-smelling. Causes Prevention and Treatment Diarrhea • Notify your health care provider if you are experiencing vomiting, fever, or diarrhea Vomiting that lasts longer than 24 hours, a sudden decrease in urine output, dizziness, or an Fever altered mental state. • Record the amount of water and formula Excessive sweating or drooling that you are taking each day and make note of the color and odor of the urine. Inadequate water intake • Ask your health care provider how much extra water (free water) you should be taking on a daily basis. Extra water can be Excessive urination given through the feeding tube using a syringe or feeding bag. Urine Dehydration Reference 1 Good Look for: n Increased thirst 2 Good n Dry lips 3 Fair n Dry and warm skin 4 Dehydrated n Rapid weight loss 5 Dehydrated n Weakness 6 Very dehydrated n Dark, strong-smelling urine n Dizziness upon standing 7 Severely dehydrated When dehydration is present, urine becomes darker and more concentrated. Guide to Adult Tube Feeding | 21
 Guide to Adult Tube Feeding at Home Page 22 Page 24
Guide to Adult Tube Feeding at Home Page 22 Page 24